-
Why Did Online Video Consumption Spike in 2009?
If you want to get a sense of how significant an inflection year 2009 was for online video, have a look at the chart below.
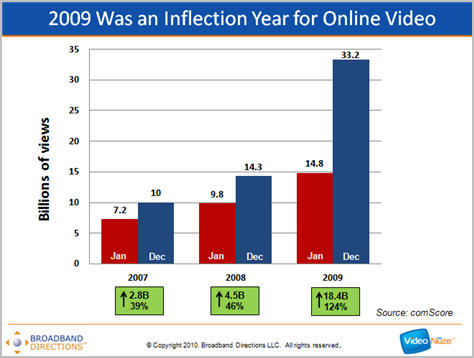
As you can see, according to comScore data, while Jan-Dec growth in 2007 (up 2.8 billion views or 39%) and 2008 (up 4.5 billion views or 46%) were impressive by any standard, the Jan-Dec 2009 growth of 18.4 billion views, up 124%, completely blows them away. Growth was so significant in 2009 that I think years down the road it will be pointed to as the year that online video really turned the corner.
But if that's the case, the question begs, "Why did growth accelerate so much in 2009 vs. prior years?" That's what I've been asked several times by industry colleagues since posting "comScore Data Shows 2009 Was a Blistering Year for Online Video" 2 weeks ago. It's a great question and though I don't have a really precise answer, here's my best sense of what happened.
No surprise, the most important contributor to the year's growth was YouTube. It zoomed from 6.3 billion views in Jan '09 to 13.2 billion in Dec. '09. That increase of 6.9 views accounts for 38% of the 18.4 billion delta between Jan and Dec. So what did YouTube do to generate such significant growth? Part of the reason is surely organic; more people uploading, sharing and viewing YouTube videos. But in 2009 YouTube also made strides in professionalizing the content on YouTube, broadening its value proposition to users. For example, its "Content ID" program, which lets media companies manage and monetize user-uploaded videos, has largely addressed the copyright infringement concerns from past years (the Viacom suit is a notable exception).
In 2009, among other things, YouTube also signed up Disney/ESPN, Univision and others as content partners, began implementing FreeWheel's ad system so 3rd party content providers could better monetize their views, engaged a number of leading brands to use it as a promotional platform, and with "YouTube Direct" engaged news organizations as partners. In short, YouTube continues to immerse itself into the fabric of the Internet. Whether users are viewing videos at its site or through its wildly popular embeds, YouTube has become omnipresent. YouTube now also claims to be the 2nd largest search site.
A second, but distant contributor to 2009's growth was Hulu, which saw its views increase by over 763 million from Jan to Dec, accounting for about 4% of the 18.4 billion increase in total views during that period. Hulu's mindshare leaped following its 2009 "Evil Plot" Super Bowl ad featuring Alec Baldwin and the subsequent ones. No doubt the addition of ABC programs throughout the year, plus other new content partners, also helped generate more viewership, along with the hugely popular SNL clips.
Once you get beyond these top 2 sites, the individual contributions to 2009's growth are more dispersed. The comScore data shows that across all video sites, usage intensified significantly during the year. For example, the number of videos viewed per viewer increased from 101 in Jan to 187 in Dec. The number of minutes watched jumped from 356 in Jan (almost 6 hours) to 762 in Dec (more than 12 1/2). There were also 31 million more U.S. Internet users watching video in Dec vs. Jan (178 million vs 147 million).
Looking beyond the numbers and thinking more qualitatively, it's also fair to conclude than in '09 online video reached a certain level of awareness that made it almost ubiquitous. There is just so much video online, and it is shared so widely, and highlighted so frequently by mainstream media, that it is unavoidable, even for the least technically-savvy among us. People are increasingly entertaining themselves with online video, but they're also finding new uses for it in their daily personal and professional lives.
I think it's unlikely we'll see the same level of growth in 2010 as in 2009, but I do believe the growth curve over the next 5 years will be very steep. The primary contributor will be convergence devices (e.g. game consoles, Blu-ray players, Roku, etc.) that are bridging online video to the TV where longer-form consumption will be the norm. Another key contributor will be TV Everywhere services, which are just now getting off the starting blocks. Lastly, I think growth in mobile consumption will be another important contributor. Add them all up and the 33.2 billion videos viewed in Dec. '09 will look relatively small 5 years from now.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Aggregators
Topics: comScore, Hulu, YouTube
-
Wal-Mart's Acquisition of Vudu Makes Little Difference
Yesterday's announcement by retailing giant Wal-Mart that it was acquiring Vudu, the on-demand movie service, generated a flurry of reactions from industry commentators. Some think it gives Wal-Mart the juice it needs to finally be a major digital media player. Others believe that Wal-Mart's miserable record in digital media suggests that the deal will be much ado about nothing. I'm in the latter camp, but not because of Wal-Mart's track record, but rather because of Vudu's own shortcomings.
Vudu's problem is that its value proposition is hamstrung by both the deals the Hollywood studios insist on to give Vudu access to their titles and by the current state of technology. Each of Vudu's 2 movie delivery
 models - rental and download-to-own - has its own problems that severely curtail its consumer appeal. No matter how slick the service looks or how many CE devices it's embedded in, consumers will readily see these drawbacks and resist embracing Vudu.
models - rental and download-to-own - has its own problems that severely curtail its consumer appeal. No matter how slick the service looks or how many CE devices it's embedded in, consumers will readily see these drawbacks and resist embracing Vudu.The rental model is primarily handicapped by the ongoing provision that the rental period "expires" 24 hours after the movie was started. That means that if real life (e.g. a crying child, a call from an old friend, a household emergency) interrupts the Vudu's users' planned viewing window, they're out of luck. It's an absurd restriction, but all online movie rentals are laboring under it. Then there's the provision that most new releases aren't available for rental until 30 days after they debut on DVD. This kind of delay doesn't mean as much for a subscription service like Netflix (which of course just agreed to a new 28-day "DVD sales window" with Warner Bros.), because it has a huge back catalog to offer. But for Vudu (and Redbox) these delays are very noticeable to users.
The download-to-own model is even more challenged. First off, tech-savvy and value-conscious consumers are increasingly focused on cost-effective rentals or subscriptions, not purchasing films. The demise of DVD sales is ample evidence of this. The idea of creating a movie "collection" in a fully on-demand world is already on the verge of seeming as archaic as creating a CD collection has been for a while. And with download-to-own prices of approximately $20, which are more than a DVD costs, consumers will be even more hesitant.
But the real killer for download-to-own is the technology limitations, more specifically the lack of portability and interoperability. Say you're actually inclined to own movies using Vudu. What do you do, download them to an external hard drive? And when you travel, do you lug that thing around with you? When you get to your destination, what device will actually let you play back your movie from your hard drive? The issues go on. The reality is that ubiquitous, cheap DVD players and the compact size of the discs themselves have created a very high bar for digital delivery to exceed. "Digital locker" concepts like DECE and Disney's KeyChest are desperately needed to move digital downloads along, but even they are just a part of a larger CE puzzle.
So, although the Vudu service is very impressive, with a slick user experience and really nice quality video, the reality is that unless Wal-Mart is able to break through these challenges, the Vudu service is going to be marginally attractive to consumers at best. That means the Wal-Mart acquisition, in fact, makes little difference.
Maybe Wal-Mart has the clout to move the studios, but given mighty Apple's own difficulties doing so, I'm skeptical that Wal-Mart will have better luck. I continue to believe that Netflix's model - which combines the full selection of DVDs with the convenience and growing selection of online delivery (including TV shows by the way) - is a far better approach. Netflix may not have all the HD and user interface bells and whistles that Vudu has, but it's a far better value proposition for consumers. This is partly why Netflix has doubled in size, to 12.3 million subscribers, in the last 3 years.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Deals & Financings, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Apple, DECE, Disney, KeyChest, Netflix, VUDU, Wal-Mart
-
Online Video Reaches the College Admissions Process
Settling in over breakfast yesterday with the Sunday Boston Globe (yes, I actually still read my hometown newspaper in print), I was intrigued by a story featured prominently on page 1 , detailing how Tufts University, a highly-selective college in the Boston area, has encouraged freshman applicants to submit one-minute "video essays" of themselves. Of the 15,436 applicants this year, over 1,000, or 6% submitted one.
Talk about a college in synch with the YouTube/Facebook generation. Not only does the idea cater perfectly to what kids today are already doing a lot of online, it provides the admissions office with an unvarnished insight into the kids, talking about what makes them special, in their own unique and creative way.
Video is an emotional medium in ways that text simply is not. That has never been truer than with these
 submissions. I looked through all the videos that the Globe added to its gallery (you can also go to YouTube and enter "Tufts admissions" to see more) and they are priceless. There's aspiring engineer Michael Klinker flying a styrofoam elephant he designed (Tufts' mascot is the "Jumbo"), to the music from Disney's "Dumbo." And Amelia Downs, whose interests are math and dance, showing the moves she's invented to simulate different math concepts. Then there's Conor Buckley, pianist and Rubik's cube solver-extraordinaire, pursuing both of his passions on split-screen.
submissions. I looked through all the videos that the Globe added to its gallery (you can also go to YouTube and enter "Tufts admissions" to see more) and they are priceless. There's aspiring engineer Michael Klinker flying a styrofoam elephant he designed (Tufts' mascot is the "Jumbo"), to the music from Disney's "Dumbo." And Amelia Downs, whose interests are math and dance, showing the moves she's invented to simulate different math concepts. Then there's Conor Buckley, pianist and Rubik's cube solver-extraordinaire, pursuing both of his passions on split-screen. The videos are endearing and authentic. Most seem to have been made on a shoestring budget, featuring 17 and 18-year old kids just being themselves, doing what they love. And if you were thinking that the one-minute video idea biases toward wealthier kids, the Tufts director of admissions said that at least 60% of the videos that have been viewed were from kids applying for student aid. With video-ready digital cameras and cell phones, ubiquitous Flip videocameras plus ubiquitous low-end editing software, kids today are more video-capable then any generation in history.
I relate the Tufts admissions videos to Unigo, the Trip Advisor-like site for high school students to check out colleges through videos made by the students themselves, which I wrote about here. Both are perfect examples of what I've called "purpose-driven" user-generated video ("UGV"). What I mean by that is with millions getting comfortable making short videos just for fun and then posting them at YouTube and elsewhere, there's an opportunity to tap this experience, but direct it into specific pursuits. Other UGV examples include the Doritos Super Bowl ads and ExpoTV's "Kitchen Table Conversations" research service. I'm sure there are plenty of others.
I expect many more organizations will leverage purpose-driven UGV going forward.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: UGC
Topics: Doritos, ExpoTV, Tufts University, Unigo
-
February Has Been a Red-Hot Month for Online Video Financings
February may be the shortest month of the year, but just less than 3 weeks in, the pace of online video financings has been the hottest since I started tracking this data over a year ago. By my count there have been at least 8 financings announced this month and I suspect I've likely missed a few (please let me know if so). This week brought financings from Clicker ($11M), YuMe ($25M) and TidalTV ($16M), adding to those announced previously: Encoding.com ($1.25M), IVT ($5.5M), Voddler ($3.5M), BrightRoll ($10M) and the big whopper of the month Ustream ($75M) though this one in two tranches.
Even with limited liquidity and choppy public markets, investors continue to make big bets across the online and mobile video ecosystems because of the massive shifts in consumer behaviors, business models and technology development. In 2009 I tracked at least 64 companies raising almost $470 million in the worst venture capital market in decades. Despite investors' enthusiasm, at least 2 big craters (Veoh - $70M and Joost - $45M) prove that even startups with blue-chip teams and promising headstarts can flop in this still nascent market.Update: Make that 9 financings in February, for a total of just under $150 millon, as Vook announced just today that it has raised a $2.5M round.What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Deals & Financings
Topics: BrightRoll, Clicker, Encoding.com, IVT, TidalTV, Ustream, Voddler, YuMe
-
Synacor Delivers NBC Olympics Video to 14 Cable Operators' 9 Million Subscribers
Overshadowed this week with the launch of HBO Go is that Synacor has been powering access to the
 subscriber-only portion of NBC's Olympics video for 14 of its cable operator customers, reaching 9 million subscribers. As Synacor's CEO Ron Frankel told me earlier this week, this is the most extensive TV Everywhere authenticated access instance to date, though it is really just a continuation of the kinds of services Synacor has been offering for years.
subscriber-only portion of NBC's Olympics video for 14 of its cable operator customers, reaching 9 million subscribers. As Synacor's CEO Ron Frankel told me earlier this week, this is the most extensive TV Everywhere authenticated access instance to date, though it is really just a continuation of the kinds of services Synacor has been offering for years. Synacor has flown somewhat below the radar as it has steadily built out its content offerings, with deals with 60 different providers now in place (e.g. MLB, NHL, MTV, etc.). Synacor offers a portal to its customers which provides its cable operator customers with single sign-on access via pre-integrated billing and user ID management. This is the same way that TV Everywhere is intended to work as it rolls out. Given its experience, Synacor looks like it will be a key player in making TV Everywhere happen in 2010.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Sports
Topics: NBC, Olympics, Synacor
-
Apple Approves SlingPlayer Mobile App with 3G; Milestone for Long-Form Mobile Streaming
One other noteworthy tidbit to come out of Mobile World Congress earlier this week was that Sling Media announced it got final approval from Apple to offer its SlingPlayer Mobile App in the App Store. SlingPlayer had been held up due to network concerns, but 2 weeks ago AT&T announced that it would let the SlingPlayer app stream live over its 3G network.
Though there aren't that many Sling users, and only a subset of them will pay the hefty $29.99 price for the SlingPlayer app, its clearance is a milestone because it truly enables high-quality place-shifting of long-form programming to a mobile device. It also steals some thunder from the FLO TV value proposition and offers a
 meaningful precedent to others who might like to stream long-form programs to iPhones and other mobile devices down the road (Netflix? Hulu? Amazon?). It's somewhat of a mystery to me how AT&T's overtaxed 3G network can now support long-form video streaming when complaints are still rampant about call quality. I don't have an iPhone or a Sling box, but if a VideoNuze reader does, and downloads the SlingPlayer app, I would be very interested in hearing about your viewing experience.
meaningful precedent to others who might like to stream long-form programs to iPhones and other mobile devices down the road (Netflix? Hulu? Amazon?). It's somewhat of a mystery to me how AT&T's overtaxed 3G network can now support long-form video streaming when complaints are still rampant about call quality. I don't have an iPhone or a Sling box, but if a VideoNuze reader does, and downloads the SlingPlayer app, I would be very interested in hearing about your viewing experience.What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Devices, Mobile Video
Topics: Apple, AT&T, iPhone, Sling
-
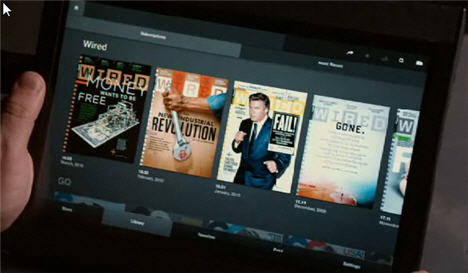
Demo of Wired Magazine Highlights iPad's Appeal
As I wrote several weeks ago, I'm skeptical of the new Apple iPad because it seems like an expensive gadget that will be hard to find mainstream buyers given its price points. Nonetheless, I thought it was a really slick device, and this week's demo of Wired magazine running on it reinforces my belief. The Wired demo, like an earlier one for Sports Illustrated, shows very tangibly how revolutionary iPad - and other tablet computers - are for print publishers. The way the editorial and advertising comes to life and readers can engage with it is quite compelling.Of course, the question still looms, will people pay $500-$800 for all that iPad coolness? Apple itself appears sensitive to the issue, clearly softening the market for possible price reductions soon after the iPad's release if volumes don't materialize. Going out on a limb a little, I for one believe we'll see an approximately $200 price reduction by holiday season '10, if not sooner. The iPad is too important to Apple and Steve Jobs to be allowed to flounder and the coming release of numerous lower-priced tablets from competitors will only add to the pressure on Apple. If iPad prices fall, it could indeed become a game-changer for Wired and other print publishers.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Devices, Miscellaneous
Topics: Apple, iPad, Sports Illustrated, Wired
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #50 - February 19, 2010
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 50th (woohoo!) edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for February 19, 2010.
This week Daisy first walks us through a piece she's writing for AdAge focused on viral video. In reviewing data on which videos have broken out online, Daisy concludes that invariably they are also supported by related advertising. In other words, viral video isn't accidental any more (if it ever was) - now it must be stoked by paid support. An example Daisy provides is for Evian's "Live Young" babies ad which has been seen online 76 million times. Evian initially promoted the ad with YouTube takeover ads. Daisy also discusses the online performance of Super Bowl ads based on Visible Measures' new Trends application, which shows a big disparity between ads that were viewed heavily online vs. rated highly when seen on TV.
Then we discuss my post, "In Trying to Preserve DVD Sales, Studios are in a Tight Spot," in which I described the lengths to which Hollywood studios are going to squeeze out the last remaining profits from DVD sales. As I explain, while the recession has had a dampening effect on DVD sales, the larger problem is that rather than buying them, increasingly consumers are expecting films to be available for rental or subscription or even for free, with ad support. A number of moves from Disney, Sony and Warner Bros. in the last week underscore the consequences studios face as they try to shore up DVD sales.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 8 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Disney, Podcast, Sony, Visible Measures, Warner Bros.